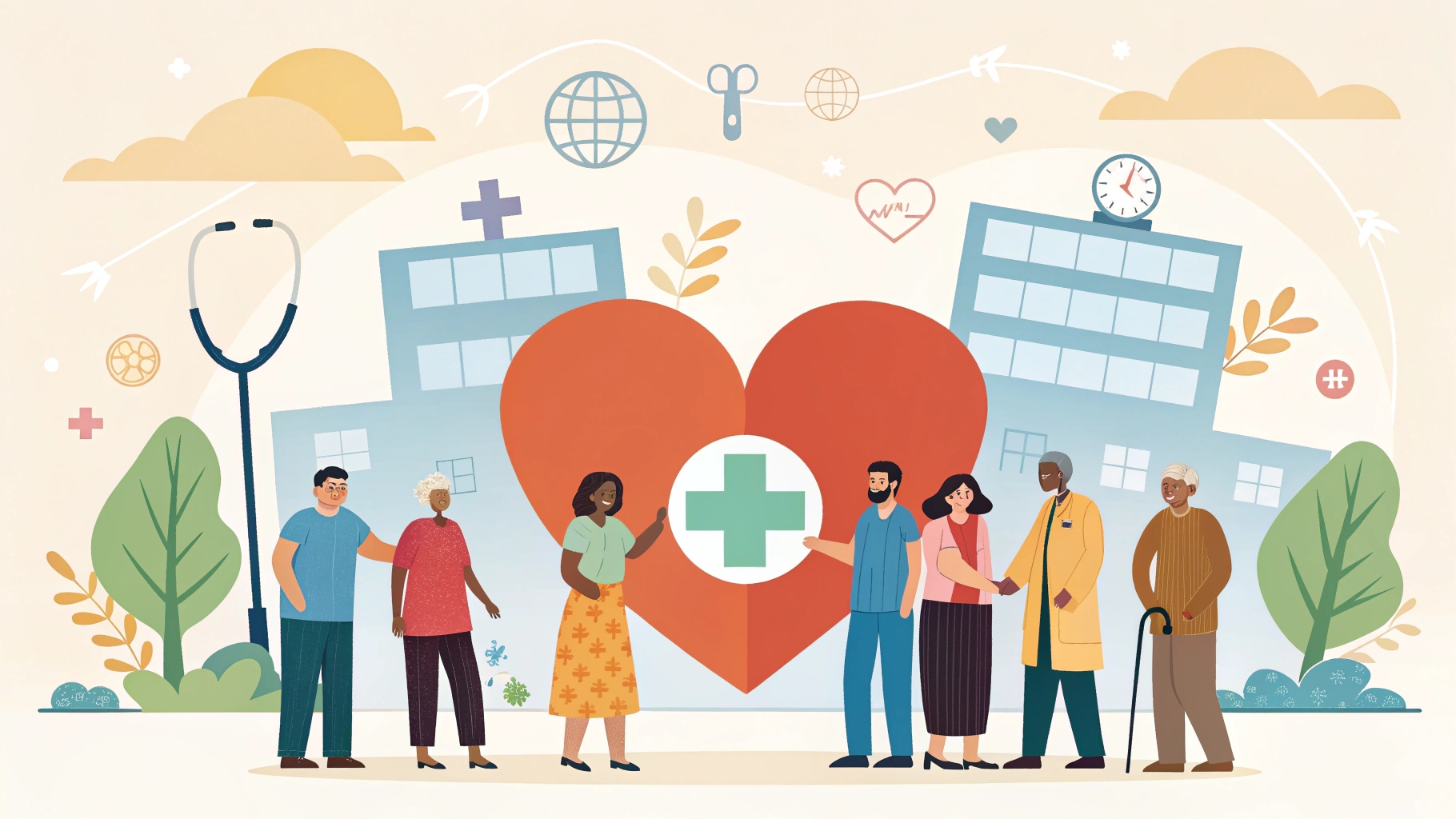
Health Equity: Fair Access to Healthcare for All
Health equity means giving every person a fair chance to be as healthy as possible. It is about removing unfair barriers that stop people from getting good healthcare. Health equity is important because without it, many people suffer from preventable diseases and poor living conditions.
Difference Between Health Equity and Health Equality
Health equality means giving everyone the same resources, like the same number of doctors or medicines. But this does not always work because different people have different needs. Health equity focuses on fairness. For example, a poor community may need extra healthcare support compared to a rich community. Equity makes sure help goes where it is needed most.
Determinants of Health Equity
Health equity depends on many factors. Social determinants like education, jobs, and safe housing affect people’s health. Economic conditions also play a big role, because low-income families often cannot afford treatment. Environmental factors such as clean water and safe air are necessary for good health. Lastly, easy access to healthcare is one of the strongest ways to build health equity.
Barriers to Health Equity
There are many challenges that block health equity. Poverty and income inequality make healthcare too costly for some people. Discrimination and racism in healthcare systems can make patients feel ignored or treated unfairly. In rural or remote areas, distance from hospitals and cultural barriers make it hard for people to get proper care.
Strategies to Promote Health Equity
To improve health equity, governments must make strong policies that support fair healthcare. Community-based interventions, such as local health centers and awareness programs, are also very helpful. Education plays a key role because informed people can take better care of themselves and demand fair treatment. Together, these strategies can make healthcare systems more equal and inclusive.
Global Perspective on Health Equity
In developed countries, many people enjoy advanced healthcare, but minority groups still face inequalities. In developing countries, health equity is a bigger challenge due to lack of resources and weak healthcare systems. International organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) are working to reduce these gaps by supporting global health projects and fair policies.
Case Studies and Examples
Some regions have shown progress in health equity. For example, community clinics in rural Africa have improved access to basic healthcare for poor families. In the United States, programs that focus on maternal health in low-income neighborhoods have reduced death rates. These examples show that targeted efforts can bring real change.
Future of Health Equity
The future of health equity depends on technology and innovation. Telemedicine allows doctors to reach patients in remote areas. Digital health records make treatment faster and more accurate. By building inclusive healthcare systems, we can make sure that no group is left behind.
Conclusion
Health equity is not just about healthcare it is about fairness, justice, and human rights. To achieve it, we must break down barriers, support communities, and create strong systems that care for everyone. A fair health system means a healthier world for all.
FAQs on Health Equity
What is the main goal of health equity?
The main goal is to make sure every person can live a healthy life, no matter their income, race, or background.
How can individuals support health equity?
People can support health equity by spreading awareness, supporting community programs, and demanding fair policies from leaders.
Why does health equity matter for communities?
It matters because healthier communities are stronger, more productive, and more united.
What are some examples of health equity initiatives?
Examples include free vaccination programs, mobile health clinics in rural areas, and education campaigns about healthy living.